Rabbit anti-Human, Mouse ASCC1 Polyclonal Antibody | anti-ASCC1 antibody
ASCC1 Antibody
IHC: 1:25-1:100
Immunohistochemistry (IHC)-Paraffin
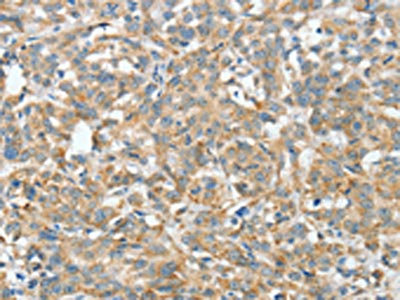
(The image on the left is immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded Human thyroid cancer tissue using MBS7125062(ASCC1 Antibody) at dilution 1/30, on the right is treated with fusion protein. (Original magnification: ×200))
NCBI and Uniprot Product Information
NCBI Description
This gene encodes a subunit of the activating signal cointegrator 1 (ASC-1) complex. The ASC-1 complex is a transcriptional coactivator that plays an important role in gene transactivation by multiple transcription factors including activating protein 1 (AP-1), nuclear factor kappa-B (NF-kB) and serum response factor (SRF). The encoded protein contains an N-terminal KH-type RNA-binding motif which is required for AP-1 transactivation by the ASC-1 complex. Mutations in this gene are associated with Barrett esophagus and esophageal adenocarcinoma. Alternatively spliced transcripts encoding multiple isoforms have been observed for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2011]
Uniprot Description
ASCC1: Enhances NF-kappa-B, SRF and AP1 transactivation. In cells responding to gastrin-activated paracrine signals, it is involved in the induction of SERPINB2 expression by gastrin. Defects in ASCC1 may be a cause of Barrett esophagus (BE). A condition characterized by a metaplastic change in which normal esophageal squamous epithelium is replaced by a columnar and intestinal-type epithelium. Patients with Barrett esophagus have an increased risk of esophageal adenocarcinoma. The main cause of Barrett esophagus is gastroesophageal reflux. The retrograde movement of acid and bile salts from the stomach into the esophagus causes prolonged injury to the esophageal epithelium and induces chronic esophagitis, which in turn is believed to trigger the pathologic changes. Genetic variants in ASCC1 have been found in individuals with Barrett esophagus and are thought to contribute to disease susceptibility. 2 isoforms of the human protein are produced by alternative splicing.
Protein type: Transcription, coactivator/corepressor
Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 10pter-q25.3
Cellular Component: transcription factor complex; cytoplasm
Molecular Function: RNA binding
Biological Process: regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent; transcription, DNA-dependent
Disease: Barrett Esophagus