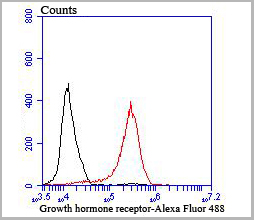
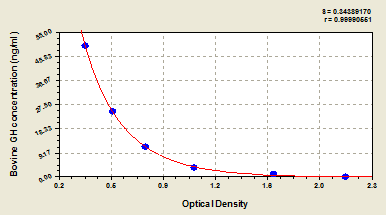
Parathyroid Hormone Synthetic Protein | PTH synthetic protein
Human Parathyroid Hormone (1-34)
Gene Names
PTH; PTH1
Purity
Greater than 98.0% as determined by RP-HPLC.
Synonyms
Parathyroid Hormone; N/A; Human Parathyroid Hormone (1-34); PTH (1-34) Human; Parathyroid Hormone (1-34) Human; Parathyrin; PTH; Parathormone; PTH (1-34); PTH synthetic protein
Purity/Purification
Greater than 98.0% as determined by RP-HPLC.
Form/Format
The protein (1 mg/ml) was lyophilized without any additives.
Sterile Filtered White lyophilized (freeze-dried) powder.
Sterile Filtered White lyophilized (freeze-dried) powder.
Sequence
H-Ser-Val-Ser-Glu-Ile-Gln-Leu-Met-His-Asn-Leu-Gly-Lys-His-Leu-Asn-Ser-Met-Glu-Arg-Val-Glu-Trp-Leu-Arg-Lys-Lys-Leu-Gln-Asp-Val-His-Asn-Phe-OH
Sequence Length
115
Solubility
It is recommended to reconstitute the lyophilized Parathormone in sterile 18M Omega -cm H2O not less than 100 ug/ml, which can then be further diluted to other aqueous solutions.
Preparation and Storage
Lyophilized Parathyrin although stable at room temperature for 3 weeks should be stored desiccated below -18 degree C. Upon reconstitution PTH should be stored at 4 degree C between 2-7 days and for future use below -18 degree C.For long term storage it is recommended to add a carrier protein (0.1% HSA or BSA).Please prevent freeze-thaw cycles.
Related Product Information for PTH synthetic protein
Description: Parathyroid Hormone Human Synthetic (C181H290N55O51S2) contains 34 amino acids and has a molecular mass of 4117.8 Dalton. The PTH is purified by proprietary chromatographic techniques.
Introduction: Parathyroid hormone (PTH), or parathormone, is secreted by the parathyroid glands as a polypeptide containing 84 amino acids. It acts to increase the concentration of calciumin the blood, whereas calcitonin (a hormone produced by the parafollicular cells of the thyroid gland) acts to decrease calcium concentration. PTH acts to increase the concentration of calcium in the blood by acting upon parathyroid hormone receptorin three parts of the body: In the bones- It enhances the release of calcium from the large reservoir contained in the bones. Bone resorption is the normal destruction of bone by osteoclasts, which are indirectly stimulated by PTH. Stimulation is indirect since osteoclasts do not have a receptor for PTH; rather, PTH binds to osteoblasts, the cells responsible for creating bone. Binding stimulates osteoblasts to increase their expression of RANKL, which can bind to osteoclast precursors containing RANK, a receptor for RANKL. The binding of RANKL to RANK stimulates these precursors to fuse, forming new osteoclasts which ultimately enhances the resorption of bone. In the kidney- It enhances active reabsorption of calcium from distal tubules and the thick ascending limb.In the intestine- It enhances the absorption of calcium in the intestine by increasing the production of vitamin D and upregulating the enzyme responsible for 1-alpha hydroxylationof 25-hydroxy vitamin D, converting vitamin D to its active form (1,25-dihydroxy vitamin D) which effects the actual absorption of calcium (as Ca2+ ions) by the intestine via calbindin.Recombinant Human full length PTH 1-84 has potential as an anti-osteoporotic agent, due to its properties as a bone formation stimulant, it increases bone turnover, stimulating osteoblasts and reducing both vertebral and non vertebral fractures.
Introduction: Parathyroid hormone (PTH), or parathormone, is secreted by the parathyroid glands as a polypeptide containing 84 amino acids. It acts to increase the concentration of calciumin the blood, whereas calcitonin (a hormone produced by the parafollicular cells of the thyroid gland) acts to decrease calcium concentration. PTH acts to increase the concentration of calcium in the blood by acting upon parathyroid hormone receptorin three parts of the body: In the bones- It enhances the release of calcium from the large reservoir contained in the bones. Bone resorption is the normal destruction of bone by osteoclasts, which are indirectly stimulated by PTH. Stimulation is indirect since osteoclasts do not have a receptor for PTH; rather, PTH binds to osteoblasts, the cells responsible for creating bone. Binding stimulates osteoblasts to increase their expression of RANKL, which can bind to osteoclast precursors containing RANK, a receptor for RANKL. The binding of RANKL to RANK stimulates these precursors to fuse, forming new osteoclasts which ultimately enhances the resorption of bone. In the kidney- It enhances active reabsorption of calcium from distal tubules and the thick ascending limb.In the intestine- It enhances the absorption of calcium in the intestine by increasing the production of vitamin D and upregulating the enzyme responsible for 1-alpha hydroxylationof 25-hydroxy vitamin D, converting vitamin D to its active form (1,25-dihydroxy vitamin D) which effects the actual absorption of calcium (as Ca2+ ions) by the intestine via calbindin.Recombinant Human full length PTH 1-84 has potential as an anti-osteoporotic agent, due to its properties as a bone formation stimulant, it increases bone turnover, stimulating osteoblasts and reducing both vertebral and non vertebral fractures.
NCBI and Uniprot Product Information
NCBI GI #
NCBI GeneID
NCBI Accession #
NCBI GenBank Nucleotide #
Molecular Weight
12,861 Da
NCBI Official Full Name
parathyroid hormone preproprotein
NCBI Official Synonym Full Names
parathyroid hormone
NCBI Official Symbol
PTH
NCBI Official Synonym Symbols
PTH1
NCBI Protein Information
parathyroid hormone; parathormone; parathyrin; parathyroid hormone 1; prepro-PTH; preproparathyroid hormone
UniProt Protein Name
Parathyroid hormone
UniProt Gene Name
PTH
UniProt Synonym Gene Names
PTH
UniProt Entry Name
PTHY_HUMAN
Similar Products
Product Notes
The PTH pth (Catalog #AAA38366) is a Synthetic Protein and is intended for research purposes only. The product is available for immediate purchase. The amino acid sequence is listed below: H-Ser-Val- Ser-Glu-Il e-Gln-Leu- Met-His-As n-Leu-Gly- Lys-His-Le u-Asn-Ser- Met-Glu-Ar g-Val-Glu- Trp-Leu-Ar g-Lys-Lys- Leu-Gln-As p-Val-His- Asn-Phe-OH. It is sometimes possible for the material contained within the vial of "Parathyroid Hormone, Synthetic Protein" to become dispersed throughout the inside of the vial, particularly around the seal of said vial, during shipment and storage. We always suggest centrifuging these vials to consolidate all of the liquid away from the lid and to the bottom of the vial prior to opening. Please be advised that certain products may require dry ice for shipping and that, if this is the case, an additional dry ice fee may also be required.Precautions
All products in the AAA Biotech catalog are strictly for research-use only, and are absolutely not suitable for use in any sort of medical, therapeutic, prophylactic, in-vivo, or diagnostic capacity. By purchasing a product from AAA Biotech, you are explicitly certifying that said products will be properly tested and used in line with industry standard. AAA Biotech and its authorized distribution partners reserve the right to refuse to fulfill any order if we have any indication that a purchaser may be intending to use a product outside of our accepted criteria.Disclaimer
Though we do strive to guarantee the information represented in this datasheet, AAA Biotech cannot be held responsible for any oversights or imprecisions. AAA Biotech reserves the right to adjust any aspect of this datasheet at any time and without notice. It is the responsibility of the customer to inform AAA Biotech of any product performance issues observed or experienced within 30 days of receipt of said product. To see additional details on this or any of our other policies, please see our Terms & Conditions page.Item has been added to Shopping Cart
If you are ready to order, navigate to Shopping Cart and get ready to checkout.